https://leetcode.com/problems/word-ladder/
Word Ladder - LeetCode
Level up your coding skills and quickly land a job. This is the best place to expand your knowledge and get prepared for your next interview.
leetcode.com
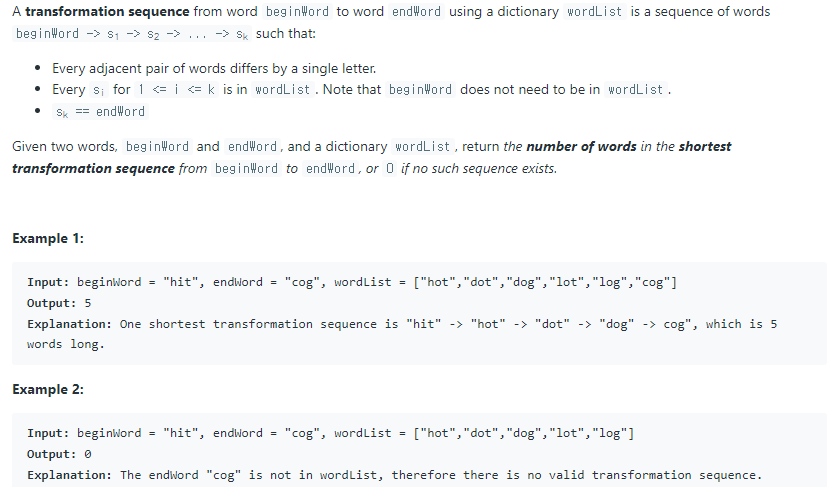
처음에는 이 문제를 재귀로 풀려고 했었는데 메모리를 초과하는 문제가 있어서 잘못된 방법이란 걸 알게 되었다.
자료구조로 딕셔너리와 큐를 사용하였다.
딕셔너리에 wordList의 모든 단어들을 한 글자씩 *로 바꾼걸 키로 하여 밸류를 리스트로 추가해준다.
ex) {*ot:'hot', 'dot', lot'}
beginWord를 큐에 담아서 앞에서부터 하나씩 꺼내면서 검사할 건데 큐에 넣을 때 level이란 걸 같이 담을 것이다.
level은 현재 몇 번째 체인이 걸렸는지 저장하는 값
while문 안에서 큐에서 꺼낸 값을
처음에 한 것처럼 각 문자 하나씩을 *로 바꿔서, 이걸 키로 딕셔너리에서 값을 가져온다.
그러면 큐에서 꺼낸 단어를 *로 바꾼 단어와 동일한 단어들을 볼 수 있다.
예를 들어 begin=hit이고 1번 인덱스를 *로 바꿨을 때 h*t이고, 이것이 키인 dict의 데이터는 {h*t:'hot'} 일 것이다.
그럼 리스트로 저장했던 밸류를 반복문으로 찾으려는 endWord랑 같으면 level+1 해서 리턴하면 된다.
그런데 hit->hot->dog->hot의 경우처럼 이미 검사한 hot을 또 검사할 위험이 있으니 visited를 만들어서 검사한 단어는 더 검사 안 하도록 해준다.
<Python>
class Solution:
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
L = len(beginWord)
allStaredWord = defaultdict(list) # {*ot:[hot, dot, lot]} 형태로 모든 wordList 저장
for word in wordList:
for i in range(L):
allStaredWord[word[:i] + "*" + word[i+1:]].append(word)
queue = deque([(beginWord, 1)])
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
while queue:
currWord, level = queue.popleft()
for i in range(L):
staredWord = currWord[:i] + '*' + currWord[i+1:] # *로 변환한 단어
for word in allStaredWord[staredWord]:
if word == endWord:
return level + 1
if word not in visited:
visited.add(word)
queue.append((word, level+1))
return 0
<JavaScript>
/**
* @param {string} beginWord
* @param {string} endWord
* @param {string[]} wordList
* @return {number}
*/
var ladderLength = function(beginWord, endWord, wordList) {
const wordDict = new Map();
const len = beginWord.length;
for(const word of wordList){
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
const stared = word.slice(0, i) + '*' + word.slice(i+1, len);
if(wordDict.has(stared)) wordDict.set(stared, [...wordDict.get(stared), word]);
else wordDict.set(stared, [word]);
}
}
const queue = [[beginWord, 1]];
const visited = new Set();
visited.add(beginWord);
while(queue.length > 0){
const [currWord, level] = queue.shift();
for(let i=0; i<len; i++){
const stared = currWord.slice(0, i) + '*' + currWord.slice(i+1, len);
if(wordDict.has(stared)){
for(const word of wordDict.get(stared)){
if(word == endWord) return level + 1;
if(!visited.has(word)){
visited.add(word);
queue.push([word, level+1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
};'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] quick sort 알고리즘: 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array (0) | 2022.04.05 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] matrix 90도 회전 알고리즘: 48. Rotate Image (0) | 2022.04.04 |
| [LeetCode] 581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray (0) | 2022.04.03 |
| [리트코드] 238. Product of Array Except Self (0) | 2022.04.03 |
| [리트코드] 이진탐색 알고리즘: 33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array (0) | 2022.04.02 |